- Responsibility
-
Responsible leadership

-
Social opinion leader


-
Responsible procurement operations


-
Research and development
-
Safety


-
Good work community


-
Shareholder value


-
Supply of electricity in Finland and climate impact


-
TVO as a company
-
Environment and climate
-
Environmental management
-
Environmental program 2019–2021
-
Results of the environmental program
-
Climate-friendly electricity
-
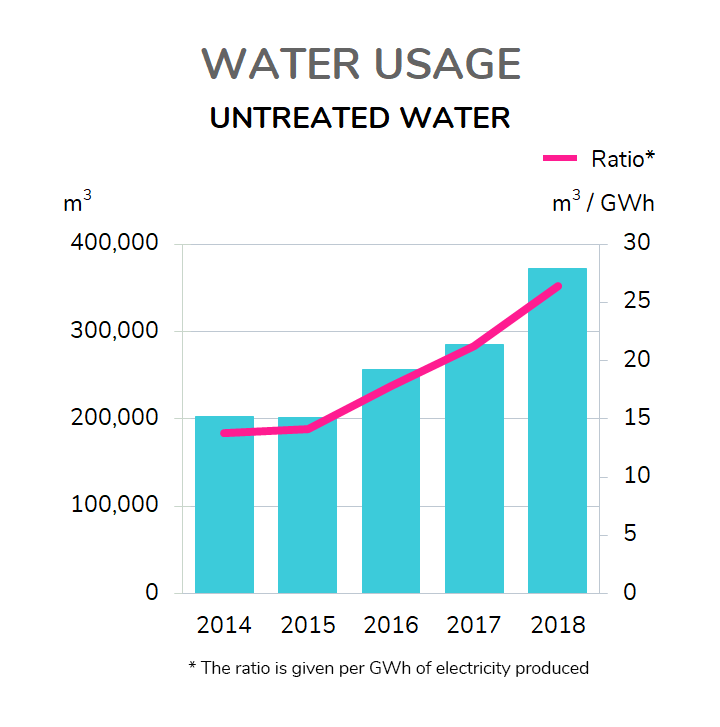
Environmental impacts
-
Cooling water
-
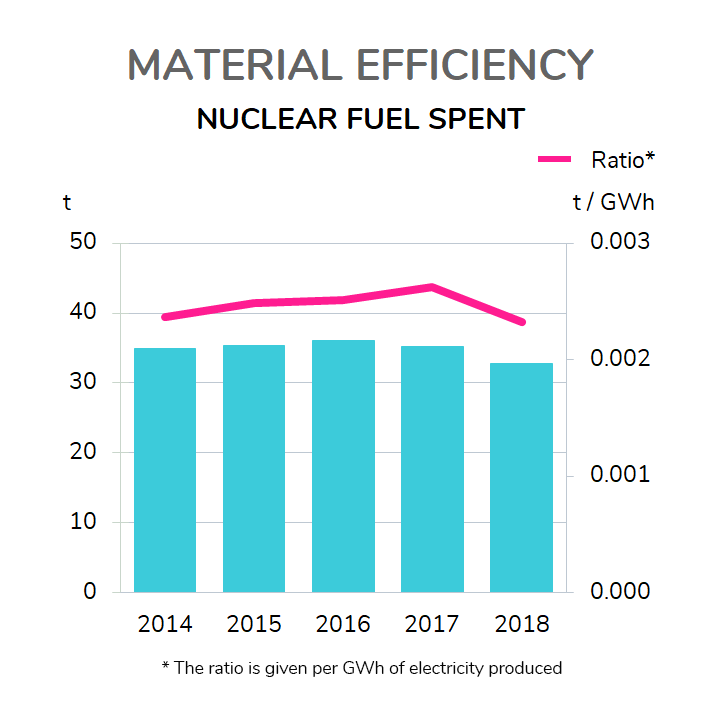
Raw materials and material efficiency
-
Production and energy efficiency
-
Emissions to the air
-
Emissions to water and soil
-
Waste
-
Environmental research and biodiversity
-
Cooperation with the authorities
-
Nuclear waste management
-
-
Responsibility reporting


- Governance
-
General
-
Shareholders' meeting
-
Board of Directors
-
Board committees
-
Committees and steering groups assisting the management
-
President and CEO
-
Management Group
-
Auditor
-
Remuneration
-
Insider administration
-
Disclosure policy for investors
-
Internal control and risk management


-
TVO Board of Directors in 2018
-
TVO Management Group in 2018
-
Organization
-
- Report of the Board of Directors
-
Main events in 2018
-
Operating environment
-
TVO as a company
-
Financial performance
-
Financing and liquidity
-
Share capital
-
Administrative principles
-
Administrative bodies
-
Regulatory environment
-
Risk management, major risks and uncertainties
-
Pending court cases and disputes
-
Nuclear power


-
Coal power


-
Research and development
-
Acquisitions of tangible and intangible assets and shares
-
Responsibility


-
Group personnel and training
-
Subsidiaries and joint ventures
-
Major events after the end of the year
-
Prospects for the future
-
Proposals to the Annual General Meeting
-
- Financial Statements
-
Key figures of TVO Group
-
Key figures of Teollisuuden Voima Oyj
-
TVO Group financial statements


-
Consolidated income statement
-
Consolidated statement of comprehensive income
-
Consolidated balance sheet
-
Consolidated statement of changes in total equity
-
Consolidated cash flow statement
-
Notes to the consolidated financial statements


- 1 General information on the Group
- 2 Accounting policies
- 3 Segment reporting
- 4 Work performed for own purpose
- 5 Other income
- 6 Materials and services
- 7 Personnel expenses
- 8 Depreciation and impairment charges
- 9 Other expenses
- 10 Finance income and expenses
- 11 Income tax expense
- 12 Property, plant and equipment
- 13 Intangible assets
- 14 Investments in joint ventures
- 15 Book values of financial assets and liabilities by categories
- 16 Loans and other receivables
- 17 Investment in shares
- 18 Cash and cash equivalents
- 19 Inventories
- 20 Derivative financial instruments
- 21 Equity
- 22 Interest-bearing liabilities
- 23 Trade payables and other current liabilities
- 24 Assets and provision related to nuclear waste management obligation
- 25 Obligations and other commitments
- 26 Related party
- 27 Financial risk management
- 28 Changes in accounting principles
- 29 Events after the balance sheet date
-
-
Parent company's financial statements


-
Parent company's income statement
-
Parent company's balance sheet
-
Parent company's cash flow statement
-
Notes to the parent company's financial statements


- 1 Accounting principles
- 2 Turnover
- 3 Work performed for own purpose
- 4 Other income
- 5 Materials and services
- 6 Notes concerning personnel and members of administrative bodies
- 7 Depreciation and impairment charges
- 8 Other expenses
- 9 Financial income and expenses
- 10 Appropriations
- 11 Non-current assets
- 12 Investments
- 13 Inventories
- 14 Current receivables
- 15 Equity
- 16 Distributable equity
- 17 Non-current liabilities
- 18 Debts due in more than five years
- 19 Current liabilities
- 20 Commitments
- 21 Derivative financial instruments
- 22 Series of shares
- 23 Carbon dioxide emission rights
-
-
Proposals to the Annual General Meeting
-
Signatures for the report of the Board of Directors and financial statements
-
Auditor's report
-
Financial information in 2019
-
Parent company's financial statements